Industrial air conditioners play a vital role in maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels in large facilities such as factories, warehouses and data centers. Understanding how these systems work can help businesses ensure efficient operations and extend equipment life.
The core of industrial air conditioning is the refrigeration cycle, which consists of four main components: compressor, condenser, expansion valve and evaporator. The process begins when the compressor compresses the refrigerant gas, increasing its pressure and temperature. This high-pressure gas then flows into the condenser, where it releases heat to the outside environment and changes into a liquid state.
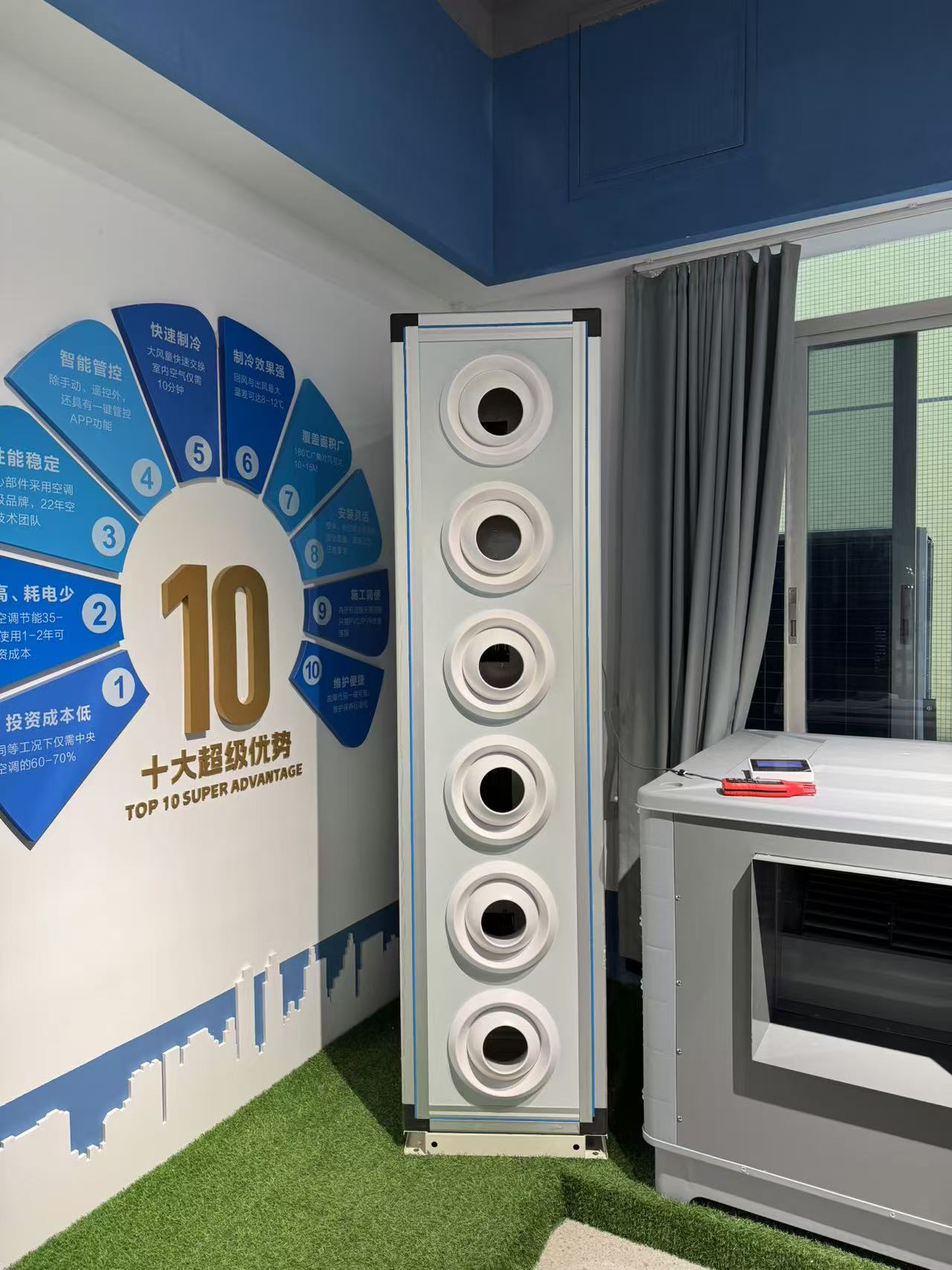
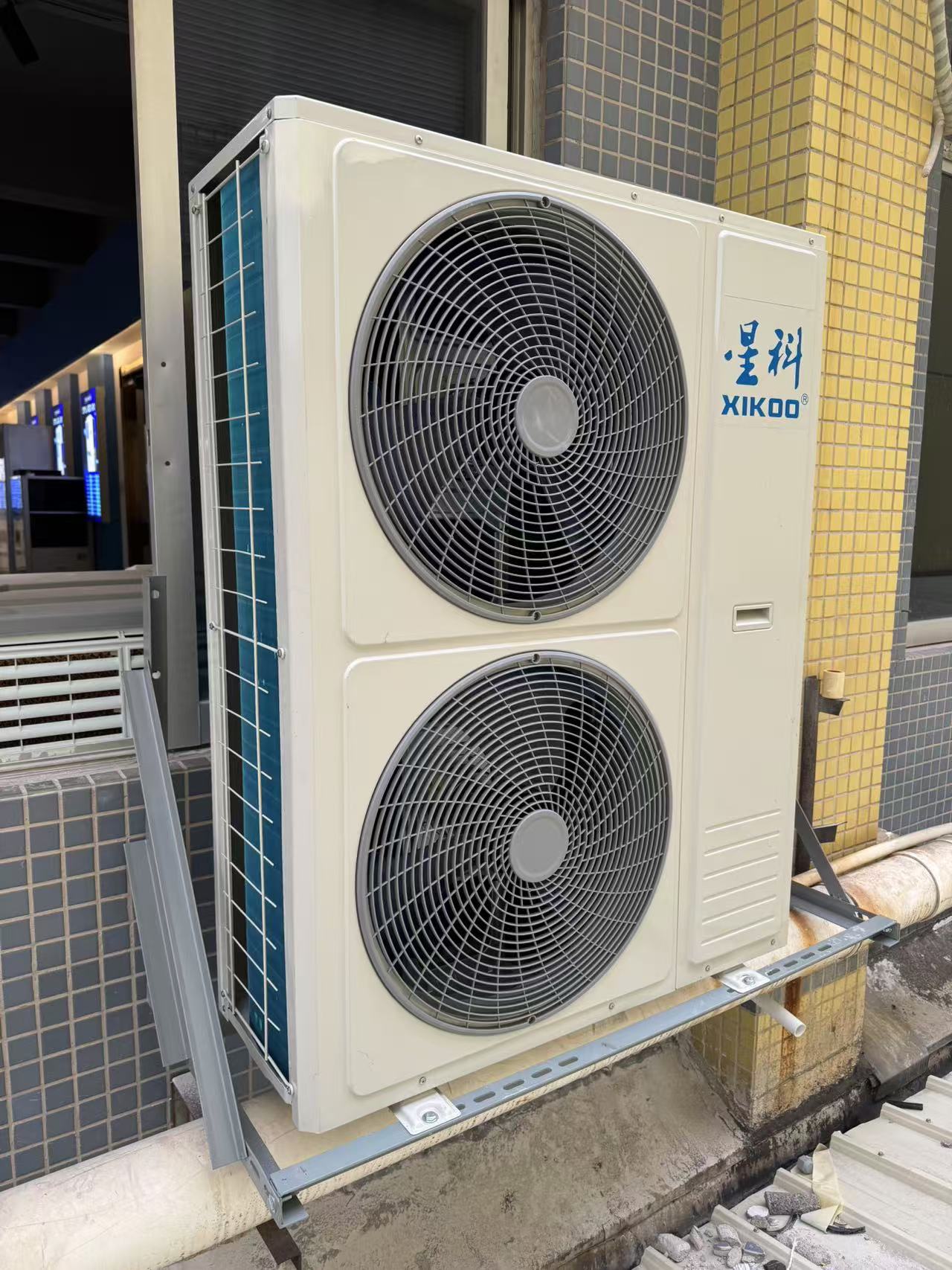


Next, the liquid refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, where the pressure drops. This pressure reduction causes the refrigerant to cool significantly as it enters the evaporator. In the evaporator, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor air and evaporates back into a gas. This heat exchange cools the air, which is then circulated throughout the facility via large fans.
Industrial air conditioners are designed to handle larger air volumes compared to residential air conditioners. They often utilize advanced control systems to monitor temperature and humidity levels to ensure the environment remains stable. In addition, many industrial systems incorporate features such as variable speed drives and energy recovery ventilators to increase efficiency and reduce operating costs.
Regular maintenance is essential for the efficient operation of industrial air conditioners. This includes cleaning filters, checking refrigerant levels, and checking components for wear. By understanding how industrial air conditioning works and implementing proper maintenance practices, businesses can create a comfortable and efficient environment while minimizing energy consumption.
Post time: Oct-30-2024